ADFS, Google, and OKTA, they all use your email address as a SAML attribute. This section handles custom SAML mapping based on either your username or an external provider key.
Important
Please be aware that configuring custom mapping attributes impacts the entire system, meaning they apply to all existing identity providers. As a result, no other provider (Azure, Windows) can work while a new mapping is set into place.
The following parameters need to be configured in this regard:
ExternalAuth.UserMappingStrategy- Defines the mapping strategy. The following options are available:ByUserEmail- Your email address is set as the attribute. This is the default value.ByUserName- Your username is set as the attribute.ByExternalProviderKey- An external provider key is set as the attribute.
ExternalAuth.UserIdentifierClaim- Defines the claim to be used as an identifier for the mapping. This is only required if you set your username as the attribute.
Custom Mapping Using OKTA
See below a configuration example for each mapping strategy using OKTA.
ByUserEmail
This is the default mapping strategy. User identification is made using an email claim. The following settings are required in the web.config file:
- Set the
ExternalAuth.Saml2.Enabledparameter toTrue. - Set the
ExternalAuth.UserMappingStrategyparameter toByUserEmail. This can be done by adding the following key inweb.config:<add key="ExternalAuth.UserMappingStrategy" value="ByUserEmail" />.
ByUserName
This enables the administrator to define a specific claim for user identification. In this example, we define a custom claim in OKTA and use user.employeeNumber as identifier.
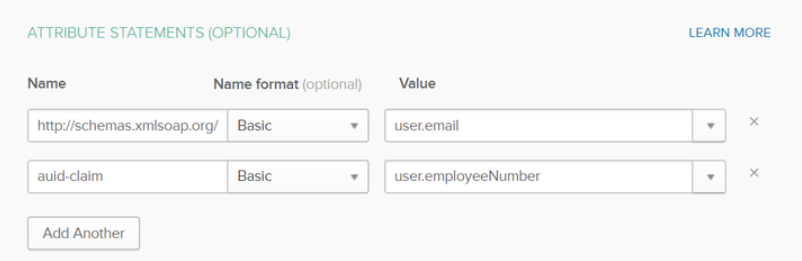
Define the corresponding attributes.
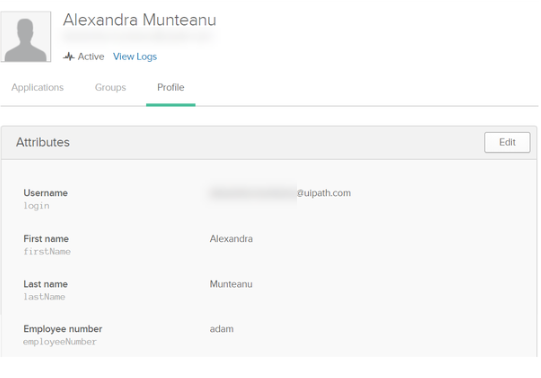
Make sure to define a user having the same username as defined in OKTA.
The following settings are required in the web.config file:
- Set the
ExternalAuth.Saml2.Enabledparameter toTrue. - Set the
ExternalAuth.UserMappingStrategyparameter toByUserName. This can be done by adding the following key inweb.config:<add key="ExternalAuth.UserMappingStrategy" value="ByUserName" />.
- Set the
ExternalAuth.UserIdentifierClaimparameter to the previously created claim, in our example,auid-claim. This can be done by adding the following key inweb.config:<add key="ExternalAuth.UserIdentifierClaim" value="auid-claim" />.
ByExternalProviderKey
This option is recommended if the users are already defined in Orchestrator and OKTA.
An administrator with access to the users database is required to run the following SQL command:
SET IDENTITY_INSERT [dbo].[UserLogins] ON
INSERT INTO [dbo].[UserLogins] (Id,UserId,LoginProvider,ProviderKey,TenantId)
VALUES (<id>,<userid>,'http://www.okta.com/exkh4xo7uoXgjukfS0h7','documentation@uipath.com',<tenantid>)
SET IDENTITY_INSERT [dbo].[UserLogins] OFF
- Set the
LoginProviderparameter to the entityId used in OKTA - Set the
ProviderKeyparameter to the user's email address
The following settings are required in the web.config file:
- Set the
ExternalAuth.Saml2.Enabledparameter toTrue. - Set the
ExternalAuth.UserMappingStrategyparameter toByExternalProviderKey. This can be done by adding the following key inweb.config:<add key="ExternalAuth.UserMappingStrategy" value="ByExternalProviderKey" />.
Updated 2 years ago