The GenericValue variable is a type of variable that can store any kind of data, including text, numbers, dates, and arrays, and is particular to UiPath Studio.
GenericValue variables are automatically converted to other types, in order to perform certain actions. However, it is important to use these types of variables carefully, as their conversion may not always be the correct one for your project.
UiPath Studio has an automatic conversion mechanism of GenericValue variables, which you can guide towards the desired outcome by carefully defining their expressions. Take into account that the first element in your expression is used as a guideline for what operation Studio performs. For example, when you try to add two GenericValue variables, if the first one in the expression is defined as a String, the result is the concatenation of the two. If it is defined as an Integer, the result is their sum.
Supported .NET Methods
| Name/Syntax | Description |
|---|---|
CompareToFunction GenericValue.CompareTo(other As GenericValue) As IntegerFunction GenericValue.CompareTo(obj As Object) As Integer | [Click here for details.][1] [1]: https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/system.string.compareto(v=vs.110).aspx |
ContainsFunction GenericValue.Contains(other As String) As Boolean | [Click here for details.][2] [2]: https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/dy85x1sa(v=vs.110).aspx Used to check whether a string variable contains a certain substring or not. For example, if you want to check if a sentence contains a specific word, the expression should be [SentenceVariable].Contains("term"), where [SentenceVariable] is the GenericValue variable containing the sentence and "term" is the word to be searched for.Note: When using this method with a GenericValue variable of data type Int, Float or Boolean, the data is automatically converted to String and handled accordingly. |
EqualsFunction GenericValue.Equals(other As GenericValue) As BooleanFunction GenericValue.Equals(obj As Object) As Boolean | [Click here for details.][3] [3]: https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/system.string.equals(v=vs.110).aspx |
GetHashCodeFunction GenericValue.GetHashCode() As Integer | [Click here for details.][5] [5]: https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/system.string.format(v=vs.110).aspx |
GetTypeFunction Object.GetType() As Type | [Click here for details.][6] [6]: https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/system.object.gettype(v=vs.110).aspx |
GetTypeCodeFunction GenericValue.GetTypeCode() As TypeCode | [Click here for details.][7] [7]: https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/system.string.gettypecode(v=vs.110).aspx |
IndexOfFunction GenericValue.IndexOf(value As String) As IntegerFunction GenericValue.IndexOf(value As String, comparisonType As StringComparison) As IntegerFunction GenericValue.IndexOf(value As String, startIndex As Integer) As IntegerFunction GenericValue.IndexOf(value As String, startIndex As Integer, comparisonType As StringComparison) As Integer | [Click here for details.][8] [8]: https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/system.string.indexof(v=vs.110).aspx Used to return the index of a substring contained inside a string variable. For example, if you want to find the index of the word "locate" inside the sentence "Find 'locate' in this sentence", the expression should be [SentenceVariable].IndexOf("locate"), where [SentenceVariable] is the GenericValue variable containing the sentence and "locate" is the term to be searched for.Note: When using this method with a GenericValue variable of data type Int, Float or Boolean, the data is automatically converted to String and handled accordingly. |
LengthFunction GenericValue.Lenght() As Integer | [Click here for details.][9] [9]: https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/system.string.length(v=vs.110).aspx Used to return the number of characters in a string variable. For example, if you want to find out how many letters a word has, the expression should be [WordVariable].Length, where [WordVariable] is the GenericValue variable containing the word.Note: When using this method with a GenericValue variable of data type Int, Float or Boolean, the data is automatically converted to String and handled accordingly. |
ReplaceFunction GenericValue.Replace(oldValue As String, new value As String) As String | [Click here for details.][10] [10]: https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/system.string.replace(v=vs.110).aspx Used to replace data contained inside a string variable. For example, if you want to change a local file path C:\ExampleFolder\Main.xaml into the corresponding server file path C:/ExampleFolder/Main.xaml, the expression should be [PathVariable].Replace("\","/") where [PathVariable] is the GenericValue variable containing the file path, "\" is the character to be replaced and "/" is the character used as replacement.Note: When using this method with a GenericValue variable of data type Int, Float or Boolean, the data is automatically converted to String and handled accordingly. |
SplitFunction GenericValue.Split(ParamArray separator As Char()) As String()Function GenericValue.Split(ParamArray separator As String()) As String()Function GenericValue.Split(separator As Char(), options As StringSplitOptions) As String()Function GenericValue.Split(separator As String(), options As StringSplitOptions) As String() | [Click here for details.][11] [11]: https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/system.string.split(v=vs.110).aspx Used to return individual components from a string variable. For example, if you want to extract the year from a MM.DD.YYYY date format, the expression should be [DateVariable].Split(".".ToCharArray)(2), where [DateVariable] is the GenericValue variable containing the date, "." is the character used as a separator, .ToCharArray is a method that creates an array with the elements delimited by the separator and (2) represents the index of the element to be returned, in our case, the year.Note: When using this method with a GenericValue variable of data type Int, Float or Boolean, the data is automatically converted to String and handled accordingly. |
SubstringFunction GenericValue.Substring(startIndex As Integer) As StringFunction GenericValue.Substring(startIndex As Integer, length As Integer) As String | [Click here for details.][12] [12]: https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/system.string.substring(v=vs.110).aspx Used to return a substring contained in a string variable. For example, if you want to extract a word from the "There are 100 machines available" sentence, the expression should be [SentenceVariable].Substring(10,3), where [SentenceVariable] is the GenericValue variable containing the sentence, 10 is the index of the first character to be returned, and 3 is the length of the substring starting from the first character. In this example, the resulted substring would be "100".Note: When using this method with a GenericValue variable of data type Int, Float or Boolean, the data is automatically converted to String and handled accordingly. |
ToBooleanFunction GenericValue.ToBoolean(provider As IFormatProvider) As Boolean | [Click here for details.][13] [13]: https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/bb346937(v=vs.110).aspx |
ToByteFunction GenericValue.ToByte(provider As IFormatProvider) As Byte | [Click here for details.][14] [14]: https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/bb355898(v=vs.110).aspx |
ToCharFunction GenericValue.ToChar(provider As IFormatProvider) As Char | [Click here for details.][15] [15]: https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/bb335877(v=vs.110).aspx |
ToDecimalFunction GenericValue.ToDecimal(provider As IFormatProvider) As DecimalFunction GenericValue.ToDecimal(format As NumberStyles) As Decimal | [Click here for details.][17] [17]: https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/bb359959(v=vs.110).aspx |
ToDoubleFunction GenericValue.ToDouble(provider As IFormatProvider) As DoubleFunction GenericValue.ToDouble(format As NumberStyles) As Double | [Click here for details.][18] [18]: https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/bb154906(v=vs.110).aspx |
ToIntFunction GenericValue.ToInt(culture As IFormatProvider) As Integer?Function GenericValue.ToInt() As Integer? | Used to convert a specified value to a nullable integer. Note: When using this method with a GenericValue variable of data type Boolean, the "True" and "False" values are converted to 1 and 0, respectively. |
ToInt16Function GenericValue.ToInt16(provider As IFormatProvider) As Short | [Click here for details.][20] [20]: https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/bb293091(v=vs.110).aspx Note: When using this method with a GenericValue variable of data type Boolean, the "True" and "False" values are converted to 1 and 0, respectively. |
ToInt32Function GenericValue.ToInt32(provider As IFormatProvider) As Integer | [Click here for details.][21] [21]: https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/bb300452(v=vs.110).aspx Note: When using this method with a GenericValue variable of data type Boolean, the "True" and "False" values are converted to 1 and 0, respectively. |
ToInt64Function GenericValue.ToInt64(provider As IFormatProvider) As Long | [Click here for details.][22] [22]: https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/bb359566(v=vs.110).aspx Note: When using this method with a GenericValue variable of data type Boolean, the "True" and "False" values are converted to 1 and 0, respectively. |
ToLowerFunction GenericValue.ToLower() As String | [Click here for details.][23] [23]: https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/system.string.tolower(v=vs.110).aspx Note: When using this method with a GenericValue variable of data type Int, Float or Boolean, the data is automatically converted to String and handled accordingly. |
ToLowerInvariantFunction GenericValue.ToLowerInvariant() As String | [Click here for details.][24] [24]: https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/system.string.tolowerinvariant(v=vs.110).aspx Note: When using this method with a GenericValue variable of data type Int, Float or Boolean, the data is automatically converted to String and handled accordingly. |
ToSByteFunction GenericValue.ToSByte(provider As IFormatProvider) As SByte | [Click here for details.][25] [25]: https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/bb342232(v=vs.110).aspx |
ToSingleFunction GenericValue.ToSingle(provider As IFormatProvider) As Single | [Click here for details.][26] [26]: https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/bb360375(v=vs.110).aspx |
ToStringFunction GenericValue.ToString(formatProvider As IFormatProvider) As StringFunction GenericValue.ToString(format As String, formatProvider As IFormatProvider) As StringFunction GenericValue.ToString() As String | [Click here for details.][27] [27]: https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/system.string.tostring(v=vs.110).aspx |
ToTypeFunction GenericValue.ToType(conversionType As Type, provider As IFormatProvider) As Object | [Click here for details.][29] [29]: https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/bb358540(v=vs.110).aspx |
ToUInt16Function GenericValue.ToUInt16(provider As IFormatProvider) As UShort | [Click here for details.][30] [30]: https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/bb337265(v=vs.110).aspx Note: When using this method with a GenericValue variable of data type Boolean, the "True" and "False" values are converted to 1 and 0, respectively. |
ToUInt32Function GenericValue.ToUInt32(provider As IFormatProvider) As UInteger | [Click here for details.][31] [31]: https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/bb357762(v=vs.110).aspx Note: When using this method with a GenericValue variable of data type Boolean, the "True" and "False" values are converted to 1 and 0, respectively. |
ToUInt64Function GenericValue.ToUInt64(provider As IFormatProvider) As Ulong | [Click here for details.][32] [32]: https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/bb155099(v=vs.110).aspx Note: When using this method with a GenericValue variable of data type Boolean, the "True" and "False" values are converted to 1 and 0, respectively. |
ToUpperFunction GenericValue.ToUpper() As String | [Click here for details.][33] [33]: https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/system.string.toupper(v=vs.110).aspx Note: When using this method with a GenericValue variable of data type Int, Float or Boolean, the data is automatically converted to String and handled accordingly. |
ToUpperInvariantFunction GenericValue.ToUpperInvariant() As String | [Click here for details.][34] [34]: https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/system.string.toupperinvariant(v=vs.110).aspx Note: When using this method with a GenericValue variable of data type Int, Float or Boolean, the data is automatically converted to String and handled accordingly. |
TrimFunction GenericValue.Trim(ParamArray trimChars As Char()) As StringFunction GenericValue.Trim() As String | [Click here for details.][35] [35]: https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/system.string.trim(v=vs.110).aspx Note: When using this method with a GenericValue variable of data type Int, Float or Boolean, the data is automatically converted to String and handled accordingly. |
TrimEndFunction GenericValue.TrimEnd(ParamArray trimChars As Char()) As String | [Click here for details.][36] [36]: https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/system.string.trimend(v=vs.110).aspx Note: When using this method with a GenericValue variable of data type Int, Float or Boolean, the data is automatically converted to String and handled accordingly. |
TrimStartFunction GenericValue.TrimStart(ParamArray trimChars As Char()) As String | [Click here for details.][37] [37]: https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/system.string.trimstart(v=vs.110).aspx Note: When using this method with a GenericValue variable of data type Int, Float or Boolean, the data is automatically converted to String and handled accordingly. |
Example of Using a GenericValue Variable
To demonstrate how a GenericValue variable works, let us create an automation that performs different operations whose results depend on the way we define their expressions. We create two GenericValue variables of different data types and display the results in the Output panel.
- Create a new blank project.
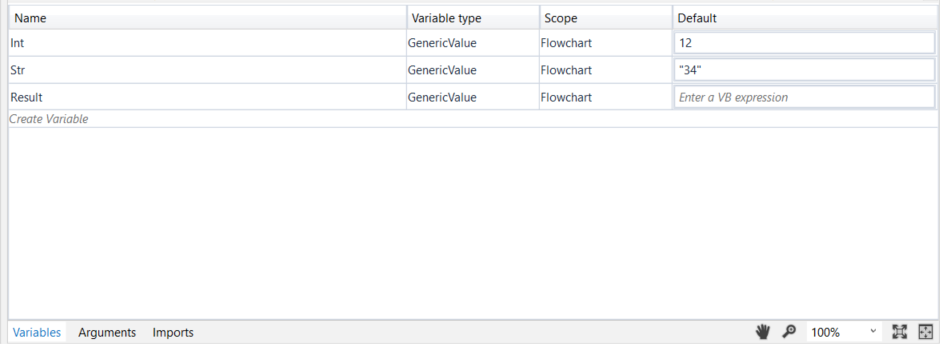
- Create three GenericValue variables:
Int,Str, andResult. - In the Default column for the
Intvariable, type 12, and for theStrvariable, type "34". The first variable is interpreted as an integer, while the second one is interpreted as a string.
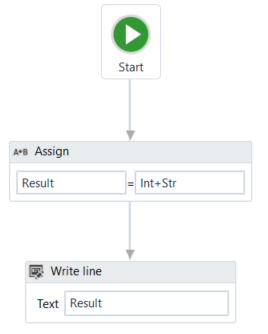
- Add an Assign activity to the Designer panel and connect it to the Start node.
- In the Properties panel, in the To field, enter the
Resultvariable. - In the Value field, type
Int+Str. - Add a Write Line activity and connect it to the Assign one.
- In the Properties panel, in the Text field, enter the
Resultvariable.
The project should look as in the following screenshot.
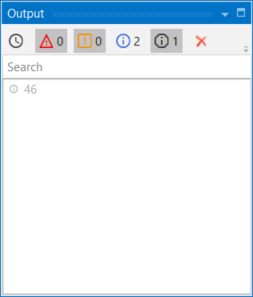
- Press F5 to execute your automation. Note that, in the Output panel, the sum of the two numbers is displayed.
- Go back to the previously added Assign activity and change the Value field to
Str+Int, to reverse the order of the variables. The project should look as in the following screenshot.
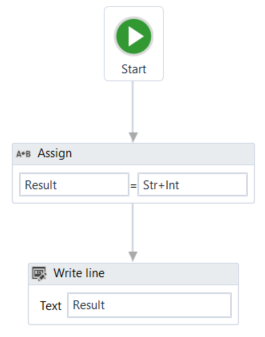
- Press F5 to execute your automation. Note that, in the Output panel, the concatenation of the two numbers is displayed.
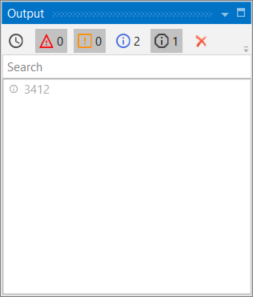
This means that UiPath Studio takes the first element defined in your expression as a guideline for what operation to perform. If the first element in your expression is an integer or a GenericValue variable filled in as integer, UiPath Studio will perform the sum of the elements.
If the first element in your expression is a string or a GenericValue variable filled in as string, UiPath Studio will perform the concatenation of the elements.
Updated 2 years ago