GIT integration in Studio requires the Microsoft Visual C++ 2015 Redistributable Update 3 x86 version. Check the Software Requirements page.
Authenticating to GIT
Authentication methods in Studio differ in accordance with the methods used for cloning a GIT repository, either HTTPS or SSH. Check this page to see which you should use if you're working with GitHub.
Notes:
- The GIT credentials you provide in Studio are stored in the Windows Credential Manager.
- The GIT integration with Studio does not currently support two-factor authentication. As a workaround, use SSO authentication method with a personal token, or the basic access authentication method.
The current guide details the steps for authenticating to a GitHub repository, but the Git integration in Studio is not limited to just this service.
Over HTTPS
When cloning a remote GIT repository or copying the current project to an existing GIT repository using HTTPS for the first time, you must provide your GIT credentials. These credentials must be entered in the Use Credentials fields:
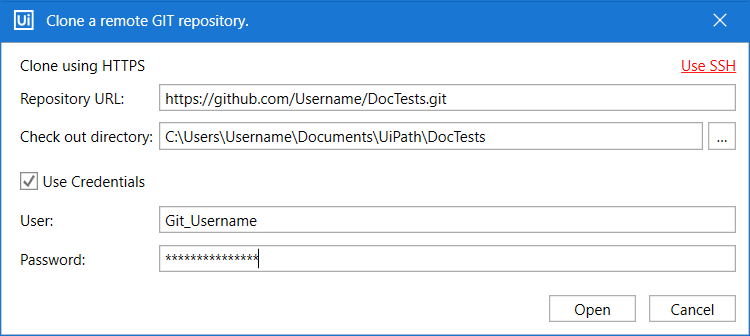
You can authenticate using:
- Username and password in their specific fields;
- Username in the User field, and GIT token in the Password field;
- GIT token in the User field, and the Password field empty.
Follow the steps detailed in this page to generate a GIT token for your GitHub repository.
Over SSH
When cloning a repository or copying the current project to an existing GIT repository using SSH for the first time, you have the option of using a private key:
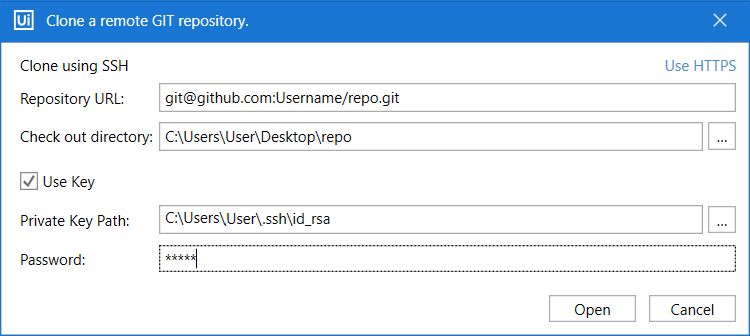
Add the Private Key Path and the Password, and then click Open to clone your remote GIT repository. Check out the steps detailed here to generate a SSH key for your GitHub repository.
Cloning a Remote GIT Repository
- In the Team tab, select Clone Repository. The Clone a remote GIT repository. window is displayed.
- Pick from Clone with HTTPS or Use SSH.
- Type in the Repository URL, and choose an empty Check out directory.
- Click the Use Credentials or Use Key checkbox to add your Git username or Private Key Path, and password.
- Click Open, Studio opens the project in the Designer panel.
- In the Open window, select a
project.jsonfile to open in Studio.
After cloning a GIT repository to a local working directory, the .git subdirectory is created containing the necessary GIT metadata. The metadata includes subdirectories for objects, refs, and template files. In addition, a HEAD file is also created, which points to the currently checked out commit.
Adding a Project to GIT
The GIT Init feature adds the current project to a local GIT repository. Access the command from the Team tab, or the status bar.
- Create or open a project in Studio. Click the Start tab > Team. The Team tab is displayed.
- Click the GIT Init button, and then select a path where the repository should be initialized. The location may be the same as the project or the parent folder. The Commit changes window opens.
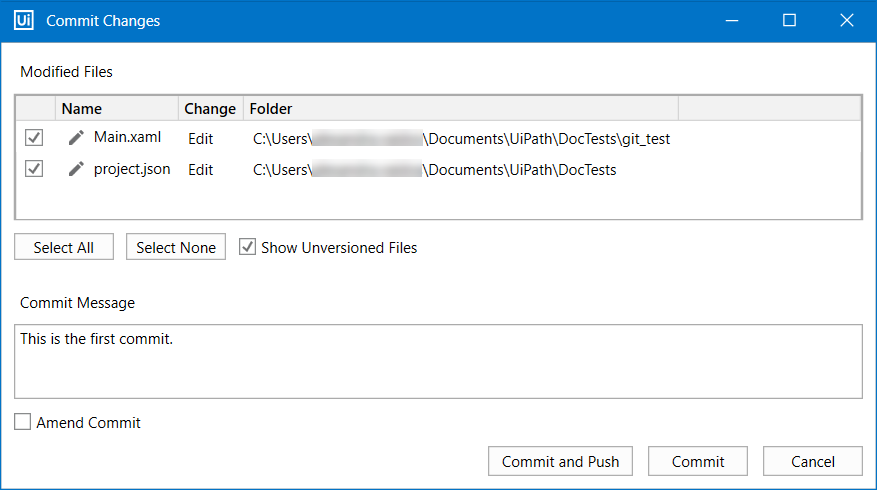
- The Modified Files section shows the project’s files that are to be added to the Git repo. Clear the box next to the ones that you don’t want to add or use Select All, Select None.
- Select the Show Unversioned Files box to add unversioned files to the list.
Write a Commit Message. Click the Commit button to commit the changes to the local Git repository.
Committing and Pushing to GIT
- From the same Commit Changes window, click the Commit and Push button to commit the changes and push them to the remote repository. This Manage Remotes window is displayed.
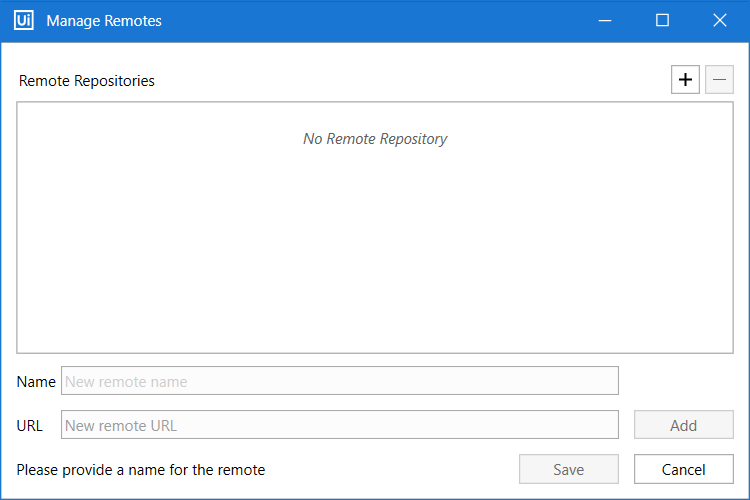
- In the Name section, add the name of the remote repository.
- In the URL section, add the remote URL.
If you want to make modifications to the added repositories, simply click an entry, change the name and URL, then click the Update button. When you're done click Add, then Save. The following message box opens. This means that the local repository is not synchronized with the remote one.
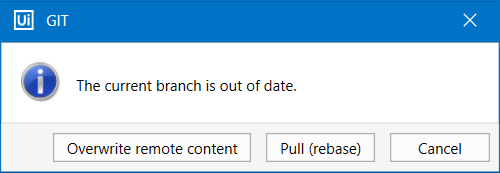
- Click the Overwrite remote content button to push the local versions of files to the remote repository and overwrite the files there.
- Click the Pull (rebase) button to pull the remote files and rebase the current branch.
- Click the Cancel button to discard the whole operation.
The number of unpushed changes, and files with uncommitted changes are visible in the status bar. Click the  icon to open the Commit Changes window, or the
icon to open the Commit Changes window, or the  icon to push changes.
icon to push changes.
Changing the Last Commit
Studio integration with Git also comes with an Amend Commit option for changing the last performed commit, before the push was performed.
- Right-click a modified file in the Properties panel and select Commit. The Commit Changes window is displayed.
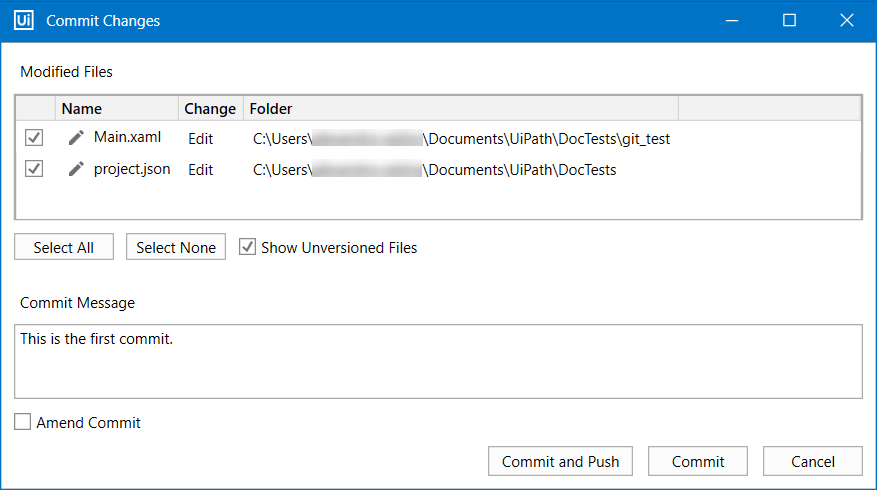
- Select the Amend Commit box. The last commit message is displayed, together with the files that were committed.
- Change the commit message and select the files that you would like to include. Click the Commit and Push or Commit button.
Undoing Pending Changes
Studio comes with the option to undo changes that have been made to versioned files, before you commit and push them to the remote repository.
After making changes to a file in the local repository, click Undo in the GIT context menu to open the Undo Pending Changes window.
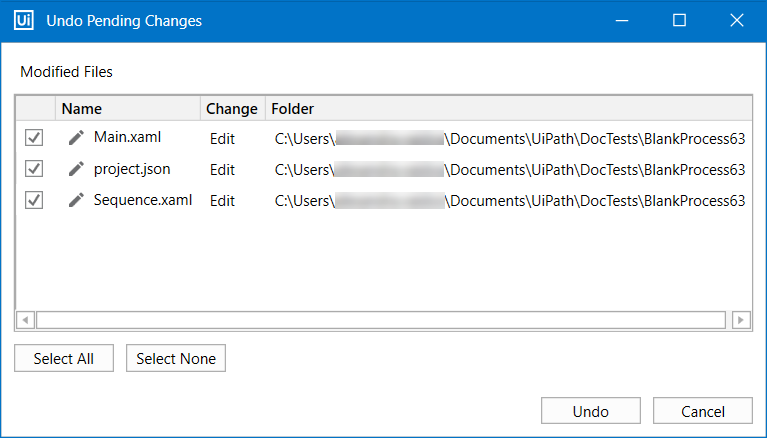
Select the checkbox next to the files and click Undo. The files are now reverted to the state before the changes were made.
Copying a Project to GIT
The Copy to GIT button in Studio Backstage view and status bar allows you to copy the current project to an existing GIT repository.
To do so first open or create a project in Studio. In the Team tab, select Copy to GIT and pick an existing GIT repository folder on your machine. The project is added to the local GIT repository and the Copy to GIT message box opens.
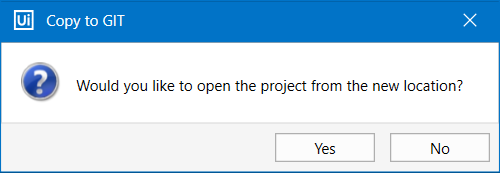
- Select Yes to open the project from the new location. The Commit Changes window opens. Write a Commit message and click Commit and Push or just Commit.
- Select No to return to the Studio user-interface.
Creating and Managing Branches
- In the Properties panel, right-click the project node or contained file, or the
 icon in the status bar and select Manage Branches. The Manage Branches window is displayed.
icon in the status bar and select Manage Branches. The Manage Branches window is displayed.
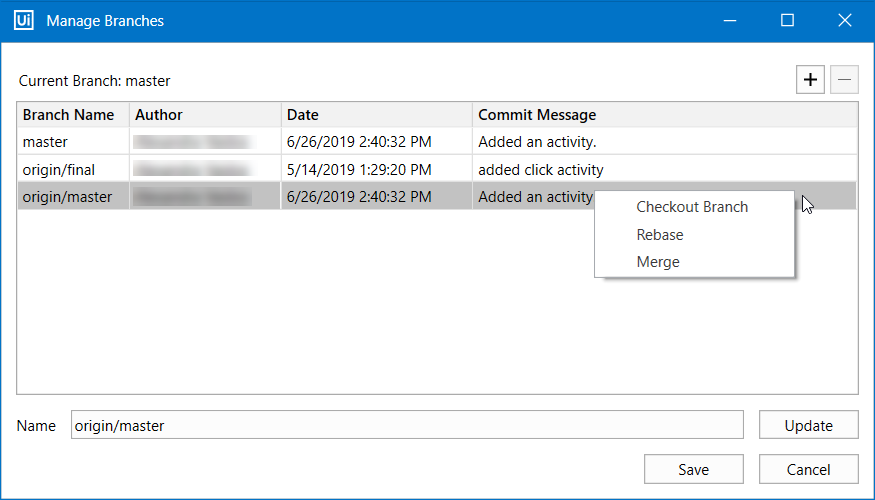
- Add a branch by clicking on the
 button. Write a name for the branch in the Name section. Click Add and then Save. The branch is added to the list.
button. Write a name for the branch in the Name section. Click Add and then Save. The branch is added to the list.
Right-click any branch to display the options for Git branches:
- The Checkout branch option switches to the selected branch.
- The Rebase option rebases the current branch onto the selected branch.
- The Merge option merges the selected branch into the current branch.
To merge a branch into the master of a GIT remote repository, you need to have the master branch checked out in Studio and then merge the modified branch into master.
To switch between branches, click the  icon in the status bar to open the list with all the recently checked out branches. Click an item to switch the branch.
icon in the status bar to open the list with all the recently checked out branches. Click an item to switch the branch.
Solving Conflicts
GIT integration with Studio comes with a feature for solving conflicts that may occur when performing the Rebase or Push command, found in the Commit Changes window.
Whenever Studio detects a conflict between the local file and the one found in the remote repository, the Solve conflicts window is displayed.
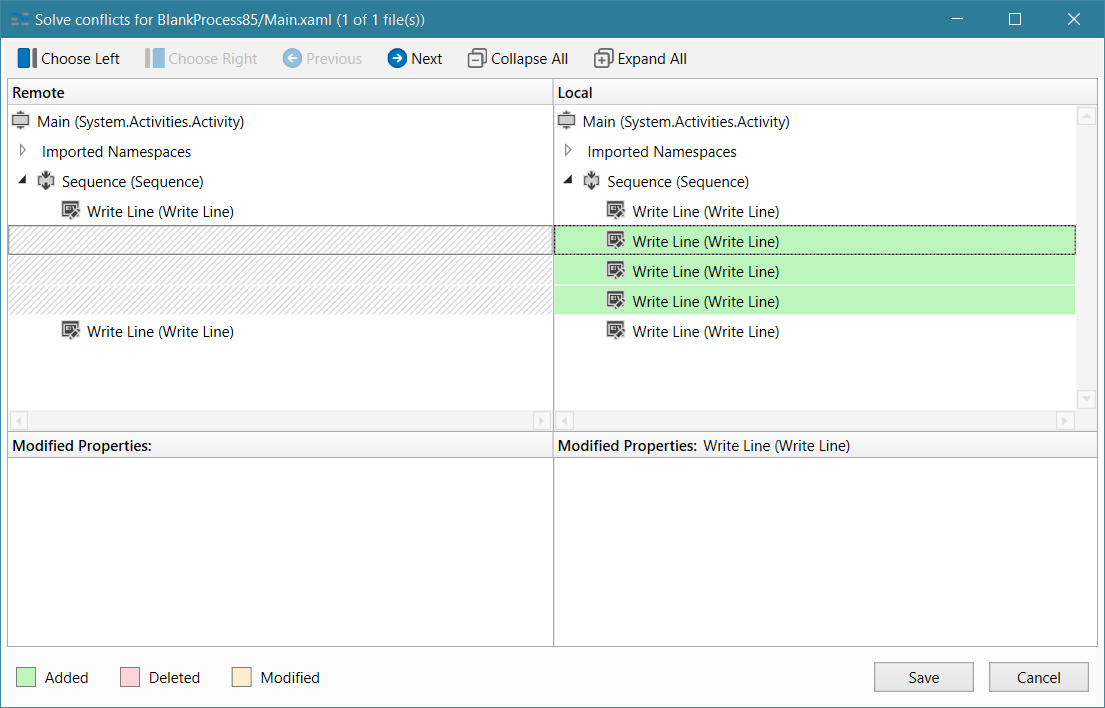
The window is similar to File Diff, showing the differences between the Remote version of the file and the Local version.
Check out field descriptions for the [Solve Conflicts] context menu here.
Disconnecting from GIT
The Disconnect option from Studio Backstage view > Team tab is available for versioned files in the following two cases:
- A process is initialized as a local GIT repository. Create a new process, use GIT Init to add it to a local GIT repository and then use Disconnect to remove the subversion tag.
- The subversion tag can be removed by clicking Disconnect for a GIT repository which includes parent and child projects.
- If you disconnect a child project, then the entire GIT repository that contains the opened project is disconnected from source control. A message box is displayed in Studio requiring your confirmation before the disconnect action is performed.
Using GIT with a Proxy Server
GIT integration in Studio supports changes to git commands for accessing remote repositories if the internet access is through a proxy server.
After obtaining the proxy settings, you need to add them to GIT configuration files in the following form:
[http "https://domain.com"] proxy = http://proxyUsername:proxyPassword@proxy.server.com:port
GIT configuration files can be found at the following locations:
configfile:%ProgramData%\Git.gitconfigfile:%UserProfile%- local
configfile from project level, for example%UserProfile%\Desktop\testproject\.git.
Updated 2 years ago